
Here, the arrangement or order of the elements matters. When you use sets to define these statistical quantities, nPr refers to the formula to solve for permutations of n elements which you take r at a time. First, they have different formulas which are: While both nCr and nPr are quantities in statistics which refer to possible subsets of a given set of objects, they aren’t totally identical. P(n,r)=n!(n−r)! What is the difference between nCr and nPr? This is why the equation for permutation is: Obviously, the numerator then becomes n!. To close this expression, multiply then divide it by (n-r)!. Since these events occur all at the same time or simultaneously, the total number of arrangements possible is the product of how many ways there are to fill each individual r place. In doing this, you will observe something interesting:įor the third place: n−2=n−(3–1) ways, and so onĪs you can see, this progression suggests that you can fill up the rth place in n−(r−1)=n−r+1 ways. Keep going until you’ve filled the nth place or until you run out of elements. Again, you can arrange the elements in the second place in n number of ways. Now you can select elements from any of the n-1 elements left for the second place.
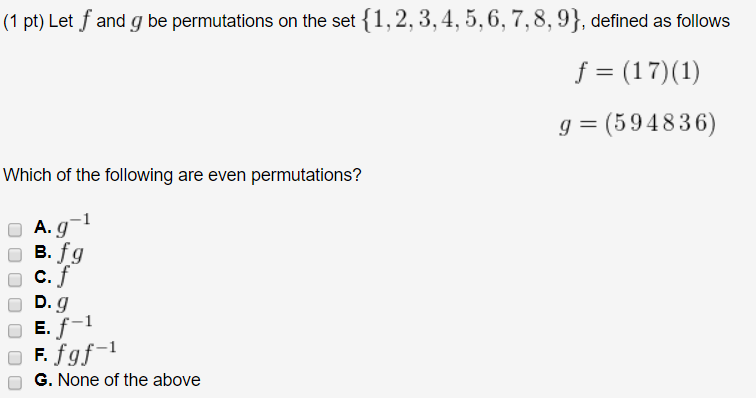
Since you’ve already filled the first place, you now have n-1 elements remaining. For these elements in the first place, you can arrange them in n ways.
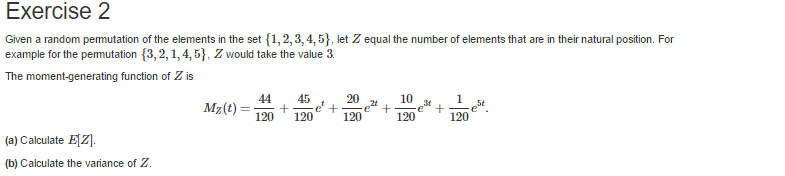
For the first place, you can fill it by selecting any of the n elements and putting them in this place. Let’s have another example to help you understand the nPr formula further. When you use the basic principle of counting, you will be more familiar with the symbol P(n,r) which is a closed expression. This is why another common form of notation of permutation is P(n,r) as seen in the permutation formula. In mathematics, it’s denoted as the r at the bottom-right corner and n at the top-left corner of P. The permutation of n elements taken r at a time also means the number of ways that you can order r objects you selected from distinct n objects in a set. Permutations differ from combinations because of the significance of the order of the elements. This means that the formula for nPr is the same as the formula for permutations which is:īy definition, permutations refer to how many ways you can get n ordered subsets of elements r from a set of elements n. nPr is the symbolic representation of permutation. What is the formula for nPr?Īs aforementioned, permutation and nPr mean the same thing. Then keep using this formula every time you need to calculate permutations manually in any given situation. Replace the numbers in the equation:Īfter performing the calculation, you can check the accuracy using the permutation calculator. In this case, you must solve for the number of ways to select 3 cards out of the total 9. Let’s apply the formula to our situation with the deck of cards. To help you understand this better, let’s go back to our earlier example. On the other hand, if you need to select all of the elements, you must modify the formula slightly. If you need to learn more about factorials or you need to perform factorial calculations, check out the factorial calculator.Īs you can see in the permutation formula, the number of permutations for when you select a single element is n. The exclamation point in the equation represents a factorial.

R refers to the number of elements you select from the given set N refers to the total number of elements in a given set Either of these allows you to calculate the number of permutations easily. You can either use the nPr calculator or the permutation formula if you want to perform the calculation manually. The good news is that you don’t have to list down all of the possible 3-digit numbers in such a case. For these three cards, how many different numbers can you come up with? Select 3 cards from the deck randomly then place them on a table in a line to create a number with 3-digits. Unlike combinations, when it comes to permutations, the order of selecting the elements has relevance.įor instance, let’s assume that you have a whole deck of cards which have numbers from 1-9. Permutation or nPr refers to the number of ways by which you can select r elements out of any given set containing n distinct objects.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
